How to choose radial electrolytic capacitors or SMD electrolytic capacitors?
2025-11-01
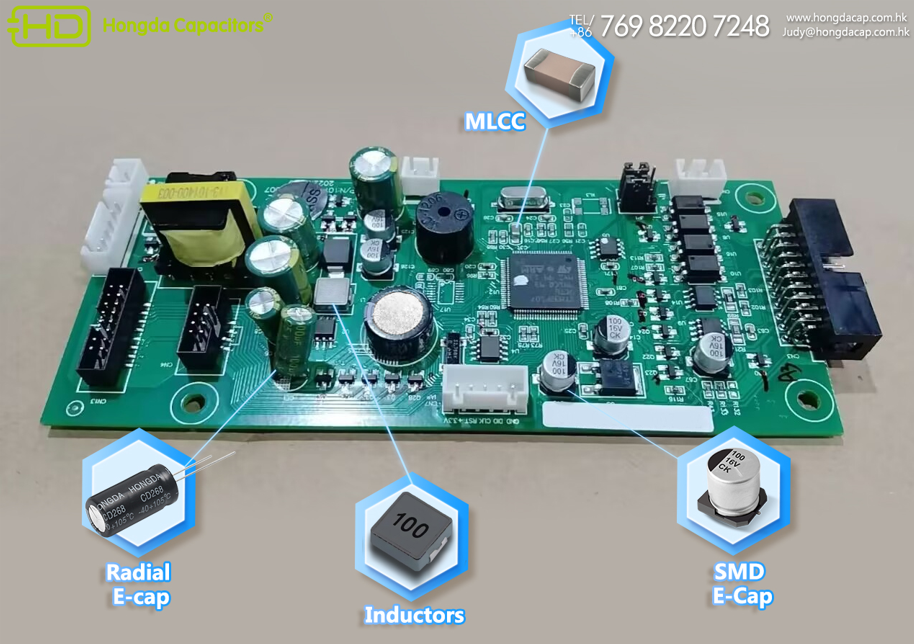
Electrolytic capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, valued for their high capacitance values and ability to handle significant voltage. Among the most common types are radial electrolytic capacitors and surface-mount device (SMD) electrolytic capacitors. While both serve the same core function—storing and releasing ectrical energy—their design, performance, and suitability for specific applications differ significantly. Choosing the right one depends on factors like space constraints, application environment, manufacturing processes, and reliability requirements. Here’s a guide to help you decide.

Understand the Core Differences
First, let’s clarify what sets these two types apart:
- Radial Electrolytic Capacitors: These are through-hole components with two leads (radial leads) extending from the same end of a cylindrical or rectangular casing. They are designed to be inserted into pre-drilled holes on a printed circuit board (PCB) and soldered to the opposite side. Their construction often allows for larger capacitance values and higher voltage ratings, making them suitable for power-intensive applications.
- SMD Electrolytic Capacitors: These are surface-mount components, meaning they attach directly to the surface of a PCB without requiring drilled holes. They have metal terminals (pads) on their base that solder to corresponding pads on the PCB. SMD designs are compact, making them ideal for miniaturized electronics.

Key Factors for Selection
Space and Form Factor
The most immediate consideration is the size of your PCB and the overall device.
- Choose SMD if: Your design prioritizes miniaturization. SMD electrolytic capacitors have a low profile (height as low as 2–3mm) and small footprint, making them perfect for compact devices like smartphones, wearables, laptops, or IoT sensors. Their surface-mount design also saves vertical space, critical for slim products.
- Choose Radial if: Space is less constrained, or you need larger capacitance/voltage ratings. Radial capacitors, while bulkier, can offer higher capacitance (up to several farads) and voltage handling (hundreds of volts), which is necessary for power supplies, amplifiers, or industrial machinery where size is not a primary concern.

Application Environment
Environmental conditions like temperature, vibration, and humidity heavily influence performance.
- Temperature Resistance: Both types have specified operating temperature ranges, but radial capacitors often excel in high-temperature environments (e.g., -40°C to +105°C or higher). This makes them better suited for industrial equipment, automotive under-the-hood systems, or power converters where heat generation is significant. SMD variants, while improving, may have narrower ranges (e.g., -25°C to +85°C) in lower-cost options, though premium SMD models can match radial ratings.
- Vibration and Mechanical Stress: Radial capacitors, with their through-hole leads, are more mechanically robust in vibrating environments (e.g., automotive, aerospace, or industrial machinery). The leads act as shock absorbers, reducing stress on the solder joints. SMD capacitors, relying on surface solder pads, are more prone to detachment under severe vibration unless reinforced with conformal coating or specialized mounting.

Manufacturing and Assembly
Your production process will also dictate the choice:
- SMD for Automated Production: SMD components integrate seamlessly with surface-mount technology (SMT) assembly lines, where pick-and-place machines and reflow ovens handle mass production efficiently. This reduces labor costs and speeds up manufacturing—ideal for high-volume consumer electronics.
- Radial for Through-Hole or Low-Volume Production: Radial capacitors require through-hole assembly, which is slower and more labor-intensive for large volumes. However, they are easier to hand-solder, making them preferable for prototyping, small-batch projects, or legacy equipment that uses through-hole PCBs.
Cost Considerations
Cost varies based on volume, specifications, and brand, but general trends apply:
- SMD electrolytic capacitors are often more cost-effective in high-volume production due to automated assembly. However, premium SMD models (with high temperature or voltage ratings) can be pricier than equivalent radial options.
- Radial capacitors may be cheaper for low-volume orders or when large capacitance/voltage values are needed, as their manufacturing process for such specs is often more mature.
Reliability and Lifespan
Electrolytic capacitors have a finite lifespan, primarily determined by temperature and ripple current.
Radial capacitors, with their larger casings, dissipate heat more effectively, potentially extending lifespan in high-temperature operations.
SMD capacitors, due to their compact size, may have shorter lifespans in harsh conditions unless designed with advanced materials (e.g., solid electrolytes instead of liquid). Solid-state SMD electrolytics, for example, offer longer lifespans and better stability than liquid-based ones, narrowing the gap with radial variants.
Application Examples
- Use SMD electrolytics in: Smartphones, tablets, LED drivers, small power adapters, and wearable devices.
- Use radial electrolytics in: Audio amplifiers, industrial power supplies, motor controllers, automotive infotainment systems (non-vibration-critical areas), and legacy electronics.

Final Guidance
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but the decision boils down to balancing your design’s needs:
Prioritize SMD for miniaturization, high-volume production, and moderate environments.
Opt for radial when you need larger capacitance/voltage, robustness in high heat or vibration, or low-volume through-hole assembly.
Always cross-check datasheets for specific ratings (temperature, voltage, lifespan) and test prototypes under real-world conditions to ensure compatibility. By aligning the capacitor type with your application’s unique demands, you’ll optimize performance, reliability, and cost.
Hongda Capacitors can offer both of the Radial Electrolytic Capacitors & SMD Electrolytic Capacitors, pls check via Email: judy@hongdacap.com.hk
Whatsapp&WeChat: +86 136 6989 7281






